If power dissipated on a current sense resistor is too high or it is difficult to find current sense resistor with the appropriate value for current limiting an additional comparator can be used as shown on figure 2b.
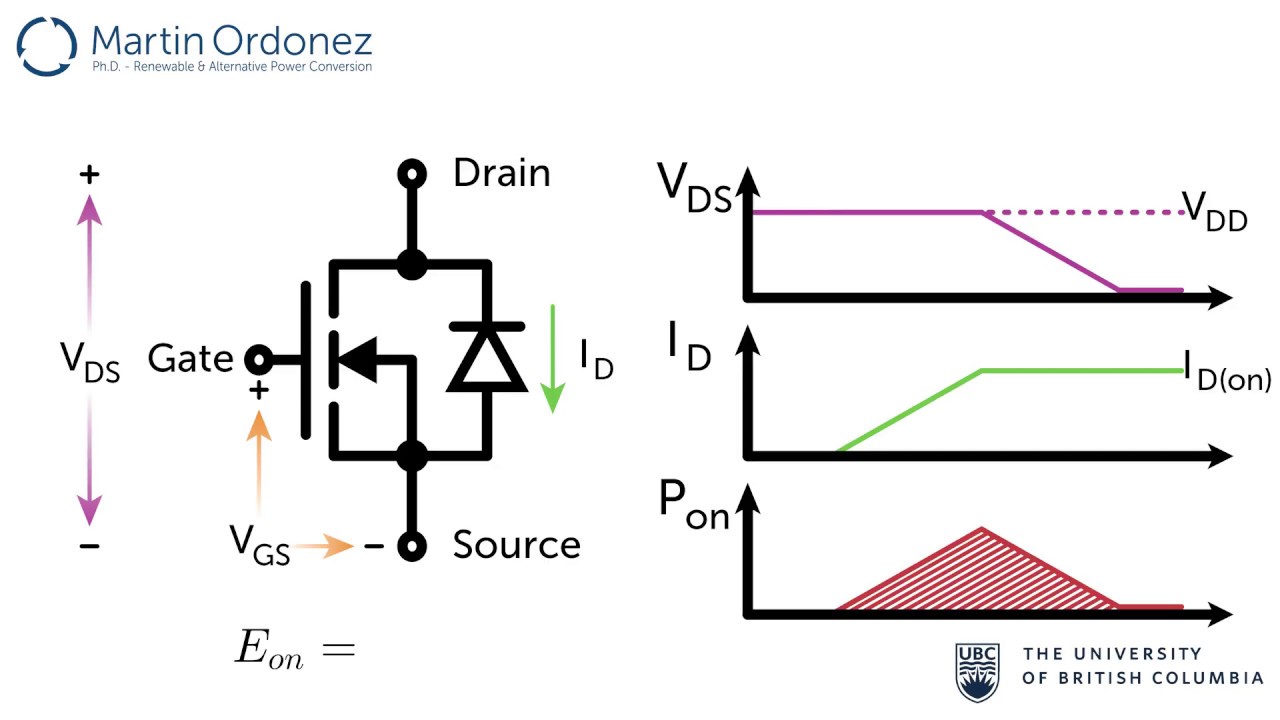
Mosfet gate driver power dissipation.
The mosfet s own.
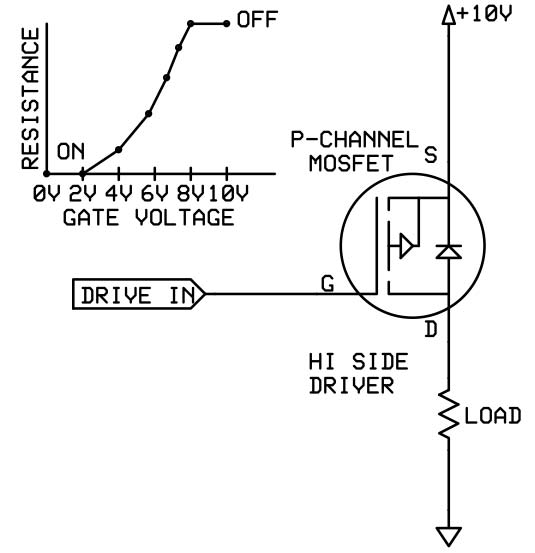
The floating channel can be used to drive an n channel power mosfet or igbt in the high side configuration which operates from 10 to 600 v.
Gate drive losses are frequency dependent and are also a func tion of the gate capacitance of the.
Switch mosfet gate losses can be caused by the energy required to charge the mosfet gate.
Most of the power is in the mosfet gate driver.
By removing the gate driver and the series resistor the slope is instead limited by the maximum source and sink currents of the pwm driver 10 ma and 25 ma respectively.
These are both turn on and turn off gate losses.
That allows direct connection of the mcu to the gate driver in case of mosfet as gate driver load with.
That is the q g tot at the gate voltage of the circuit.
Power dissipation during on time.
Therefore the maximum usable gate drive power is always derived from setups with non oscillating driver output current.
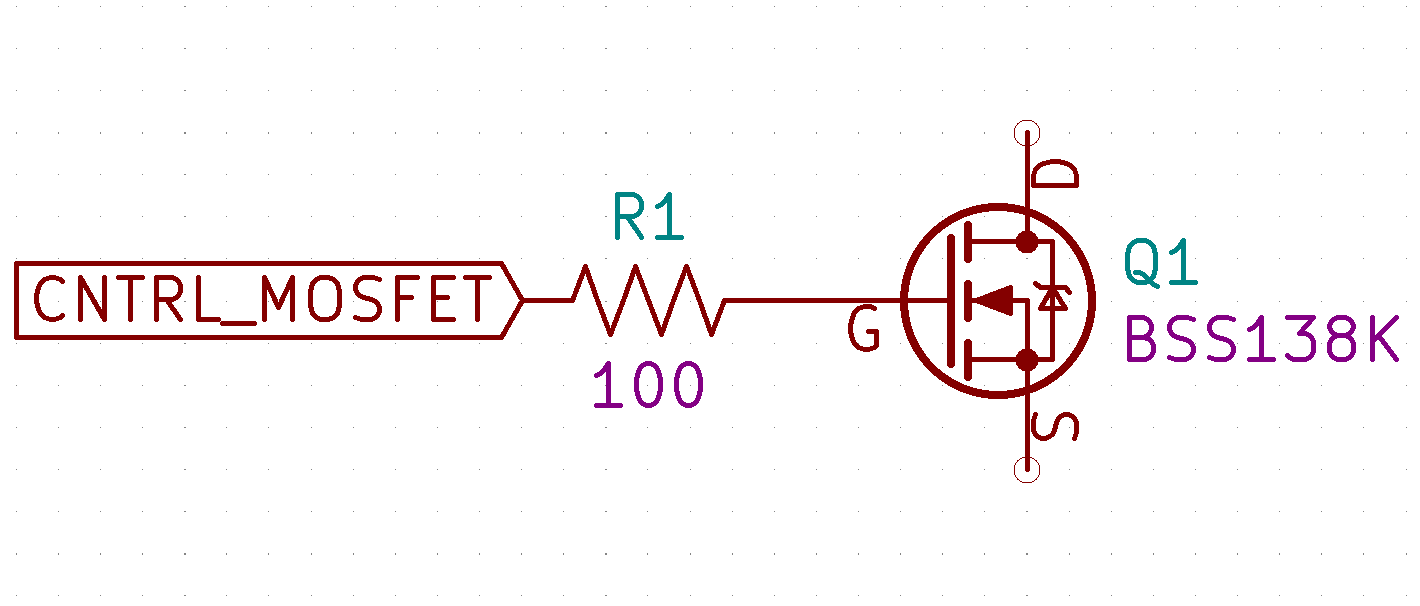
A gate driver is used when a pulse width.
The output drivers feature a high pulse current buffer stage designed for minimum driver cross conduction.
The logic input is compatible with standard cmos or lsttl output down to 3 3 v logic.
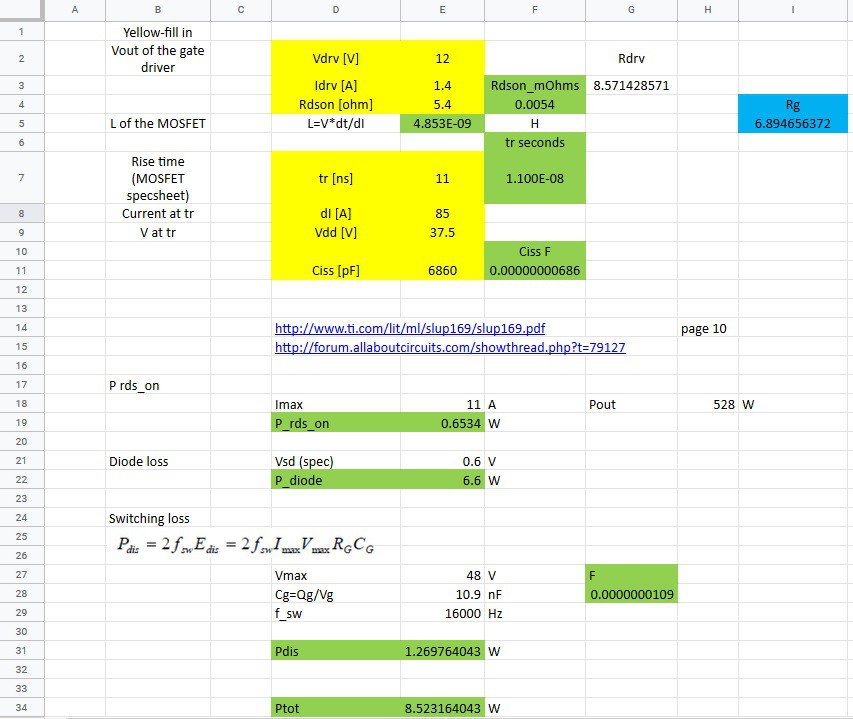
The rest of this post will show the calculations on where power is dissipated in the mosfet and compare the two designs.
Increase the gate driver current lowering switching losses.
Rc circuit model for a gate driver with mosfet output stage and power device as a capacitor.
Decades of application expertise and technology development at both infineon and international rectifier have produced a portfolio of gate driver ics for use with silicon and wide bandgap power devices such as mosfets discrete igbts igbt modules sic mosfets and gan hemts we offer excellent product families of galvanic isolated gate drivers automotive qualifies gate drivers 200 v 500 700.
Driver on off resistance can vary 10 over temperature mosfet internal gate resistance varies with mosfet temperature radiation proportional to t4 performance improves with temperature mosfet internal gate resistance diode loss and frequency related capacitance changes tend to reduce driver ic internal power dissipation.
R ds on also directly affects power dissipation internal to the driver.
Driver output current oscillations may lead to additional power dissipation in the gate driver unit due to clamping effects and non linear behaviour of the output stages and controlling circuitry.